La couleur vin est un indice essentiel sur son cépage, son processus de vinification et son potentiel de vieillissement. Certains vins affichent une robe intense, presque noire, tandis que d’autres dévoilent une teinte légère et translucide. Qu’est-ce qui explique ces différences ?
Plongeons dans les secrets des différents types de vin et découvrons l’impact de la maturation des raisins sur la couleur du nectar.
L’influence des cépages sur la couleur du vin
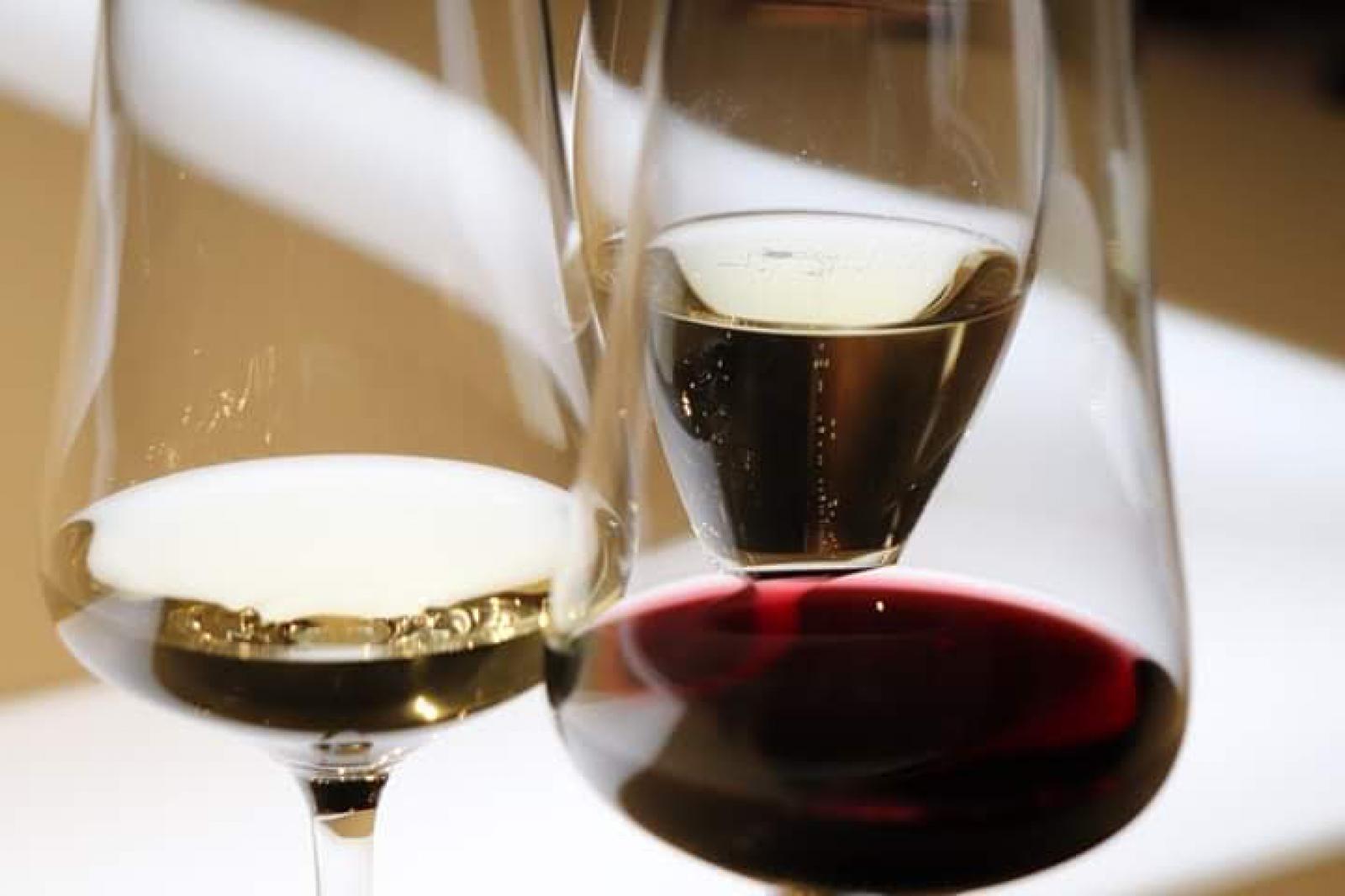

Tous les raisins ne produisent pas la même couleur de vin. Certains cépages contiennent plus de pigments, donnant naissance à des vins plus foncés.
Les cépages riches en anthocyanes
Les anthocyanes sont des pigments naturels responsables des teintes rouges et violettes du vin. Plus un raisin en contient, plus le vin sera sombre.
- Cabernet Sauvignon : réputé pour sa robe profonde et ses reflets violacés.
- Syrah : produit des vins presque noirs avec des notes épicées.
- Malbec : connu pour ses vins rouges foncés aux reflets pourpres.
- Tannat : offre une couleur dense et une forte concentration en tanins.
À l’inverse, certains cépages comme le Pinot Noir ou le Gamay donnent des vins rouges plus clairs et translucides.
L’impact de la maturation des raisins sur la teinte du vin
La maturation des raisins joue un rôle majeur dans l’intensité colorante du vin.
- Raisins récoltés tôt : ils contiennent moins de pigments et donnent des vins plus légers.
- Raisins récoltés à pleine maturité : ils concentrent les anthocyanes et les tanins, résultant en une robe plus foncée.
- Surmaturation et vendanges tardives : elles accentuent encore davantage la concentration en pigments, notamment pour certains vins rouges corsés.
Les conditions climatiques influencent aussi cette maturation. Dans les climats chauds, les raisins accumulent plus de couleur que dans les climats frais.
Le rôle de la vinification dans la couleur du vin
La durée de macération
Lors de la vinification, la durée de macération des peaux dans le jus détermine l’intensité de la couleur.
- Macération courte (quelques jours) : produit des vins rouges légers comme certains Gamay.
- Macération longue (plusieurs semaines) : donne des vins plus foncés et plus tanniques, comme ceux issus du Cabernet Sauvignon ou de la Syrah.
L’extraction des pigments
Plusieurs techniques permettent de renforcer la couleur vin :
- Pigeage : enfoncer les parties solides du raisin dans le jus pour extraire plus de couleur.
- Remontage : arroser le chapeau de marc pour intensifier l’extraction des pigments.
- Macération à chaud : accélérer la dissolution des anthocyanes dans le moût.
Certains vignerons choisissent aussi d’élever leur vin en fûts de chêne, ce qui peut assombrir la robe au fil du temps.
L’évolution de la couleur avec l’âge
Un vin ne conserve pas sa couleur d’origine indéfiniment. Avec le temps, son évolution entraîne des modifications notables.
- Les vins rouges foncés s’éclaircissent : au fil des années, ils passent du pourpre au rubis, puis prennent des teintes tuilées et orangées.
- Les vins rouges clairs s’oxydent plus vite : les cépages peu riches en anthocyanes perdent plus rapidement leur couleur.
La gestion du vieillissement en cave joue aussi un rôle. Une conservation optimale limite l’oxydation et permet aux vins de vieillir harmonieusement.
Pourquoi certains vins blancs sont plus foncés ?
Si la question de la couleur vin concerne souvent les rouges, les blancs peuvent eux aussi afficher des teintes très variées.
- Blancs jeunes et frais : ils sont généralement pâles avec des reflets verts ou dorés.
- Blancs vieillis ou oxydés : ils prennent des nuances dorées voire ambrées avec le temps.
Certains vins blancs fermentés en fûts de chêne ou soumis à une longue macération, comme les vins orange, développent une robe plus intense.
Les erreurs à éviter en interprétant la couleur du vin
Beaucoup pensent qu’un vin plus foncé est forcément meilleur ou plus puissant. Ce n’est pas toujours vrai.
- Un vin clair n’est pas forcément léger : certains Pinot Noir ou Nebbiolo sont clairs mais possèdent une grande intensité aromatique.
- Un vin foncé ne signifie pas un meilleur vieillissement : un vin riche en couleur peut aussi mal évoluer s’il manque d’acidité et d’équilibre.
L’observation de la couleur est un bon indice, mais elle doit être complétée par l’analyse des arômes et du goût.
Conclusion
La couleur vin est influencée par plusieurs facteurs : cépage, maturation des raisins, techniques de vinification et vieillissement. Elle donne des indices précieux sur le style et l’évolution d’un vin, mais ne doit pas être le seul critère d’évaluation.
En observant attentivement la robe d’un vin, on peut déjà deviner une partie de son caractère et de son potentiel de dégustation.
Si vous avez apprécié cet article, n’hésitez pas à lire l’article suivant “Comment reconnaître un bon vin à petit prix“, qui pourrait également vous intéresser !