Spring is a crucial time for viticulture. Young vine shoots are particularly sensitive to frost. Winegrowers need to act quickly to limit losses. Different vine protection techniques are available, depending on climate and available resources.
If you're interested in wine-related articles, download our app for IOS or Android. It will give you access to our wine lexicon, our articles and our innovative solution, designed for all wine consumers and collectors.
Understanding the risks associated with grapevine frost
Grapevine frost occurs when temperatures drop below zero at bud-break. Waterlogged buds crystallize and die. Losses can significantly reduce a plot's yield. In regions with a cold or unstable wine-growing climate, this risk is a recurring one. Winegrowers keep a close eye on the weather forecasts. Increased vigilance means they can take action before the damage becomes irreversible.
Weather monitoring for viticulture
Modern viticulture relies on connected weather stations. They continuously measure air and soil temperatures. Winegrowers can anticipate frost events thanks to real-time alerts. This precise monitoring of the viticultural climate guides the choice of protection method.
Antifreeze candles to protect vines
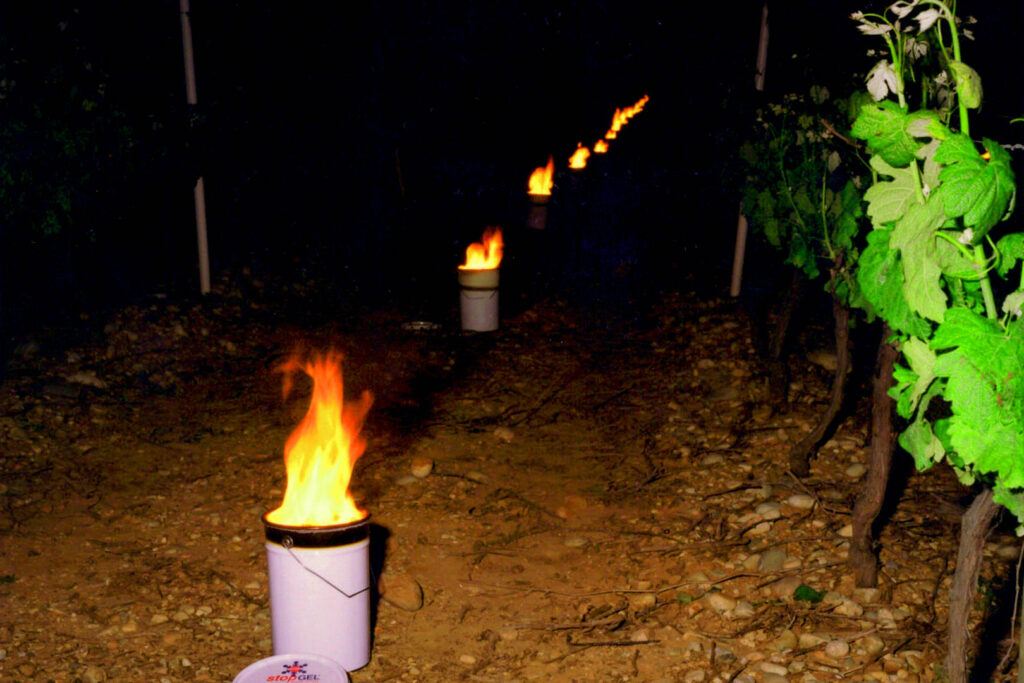

Antifreeze candles are one of the traditional techniques used to protect vines. Placed between the rows, they radiate heat. Their action slightly raises the ambient temperature around the buds. This solution is costly, but effective on critical nights. It is best suited to small plots or prestigious vintages.
Water spraying to combat frost on the vine
Sprinkling means watering vines when frost threatens. The water forms a thin film that freezes around the buds. This phenomenon protects the internal temperature of plant tissues. This viticulture technique requires an abundant water source and a suitable installation. It offers reliable vine protection, even during intense cold.
Antifreeze towers to stir the air
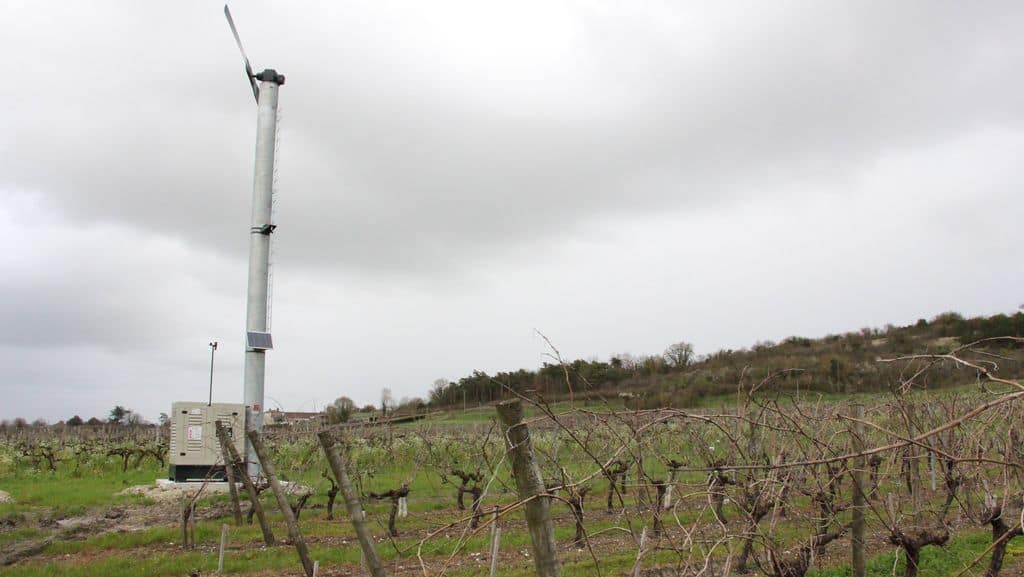

Antifreeze towers use large propellers to mix the air. They move warmer air from higher up towards the vines. This method limits the impact of vine frost on calm, clear nights. The towers run on oil, electricity or gas. They are common in vineyards with continental climates.
Mobile heaters for emergency situations
Winegrowers can install mobile heaters between the rows of vines. These devices deliver targeted heat to the buds. They are often used in conjunction with other means of vine protection. The system is costly and requires constant monitoring. It is best suited to small vineyards or high-value plots.
The role of thermal nets and blankets
In some areas, winegrowers use thermal nets or tarpaulins. These create a barrier against the night-time cold. They reduce heat loss from the soil and vines. This type of preventive viticulture works well for young plants. It does, however, require good logistical organization in the spring.
Adapting vine pruning and management
Pruning choices influence vine resistance to frost. Winegrowers sometimes delay pruning to postpone budburst. A later shoot is more likely to escape spring frosts. Vine training systems also influence air circulation in the vineyard. Good aeration limits pockets of cold air near the buds.
Tillage to optimize vine protection
Well-maintained soil captures heat better during the day. This heat is released at night, reducing the impact of vine frosts. Winegrowers can use mechanical weeding to promote this thermal accumulation. This type of tillage is part of an overall strategy of sustainable viticulture.
Selecting grape varieties suited to the winegrowing climate
The choice of grape variety is essential to limit frost losses. Winemakers sometimes opt for late-budding varieties. In a high-risk wine-growing climate, this choice reduces damage. Vine protection also involves adapting planting to local conditions.
The importance of training and exchange between winemakers
Combating frost on vines requires a sound knowledge of the methods available. Specialized training courses help professionals to optimize their vine protection. Exchanges of experience between winegrowers provide inspiration for effective solutions. This solidarity is invaluable in regions where viticulture regularly suffers losses.
If you enjoyed this article, don't hesitate to read the following article "Installing a wine cellar in a garage: steps to follow"which may also be of interest to you!